Specific Heat Capacity Definition
The heat capacity in calories per gram is called specific heat. Basics - The SI-system unit converters physical constants drawing scales and more.
Does Atmospheric Pressure Affect Specific Heat Capacity Quora
Where Q is the heat capacity in Joules.
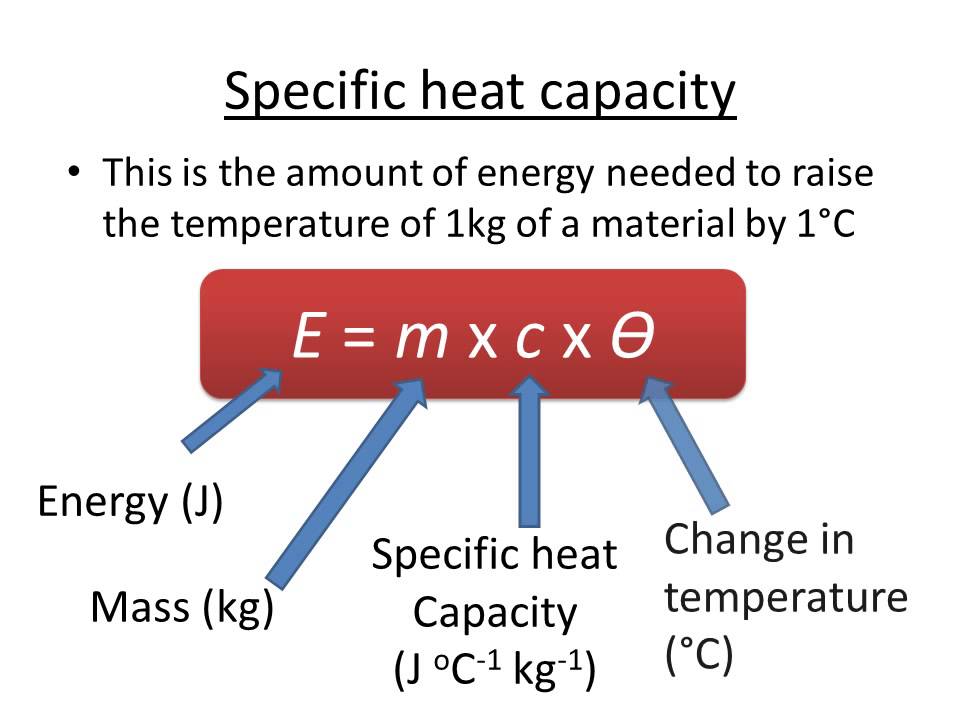
. Units of specific heat are calories or joules per gram per Celsius degreeFor example the specific heat of water. Specific heat has SI units J kg-1 K-1. The specific heat power of water is 42 joules per gram per Celsius degree.
The definition of the calorie is based on the specific heat of water defined. C p c p. It reflects the capacity to do non-mechanical work and the capacity to release heat.
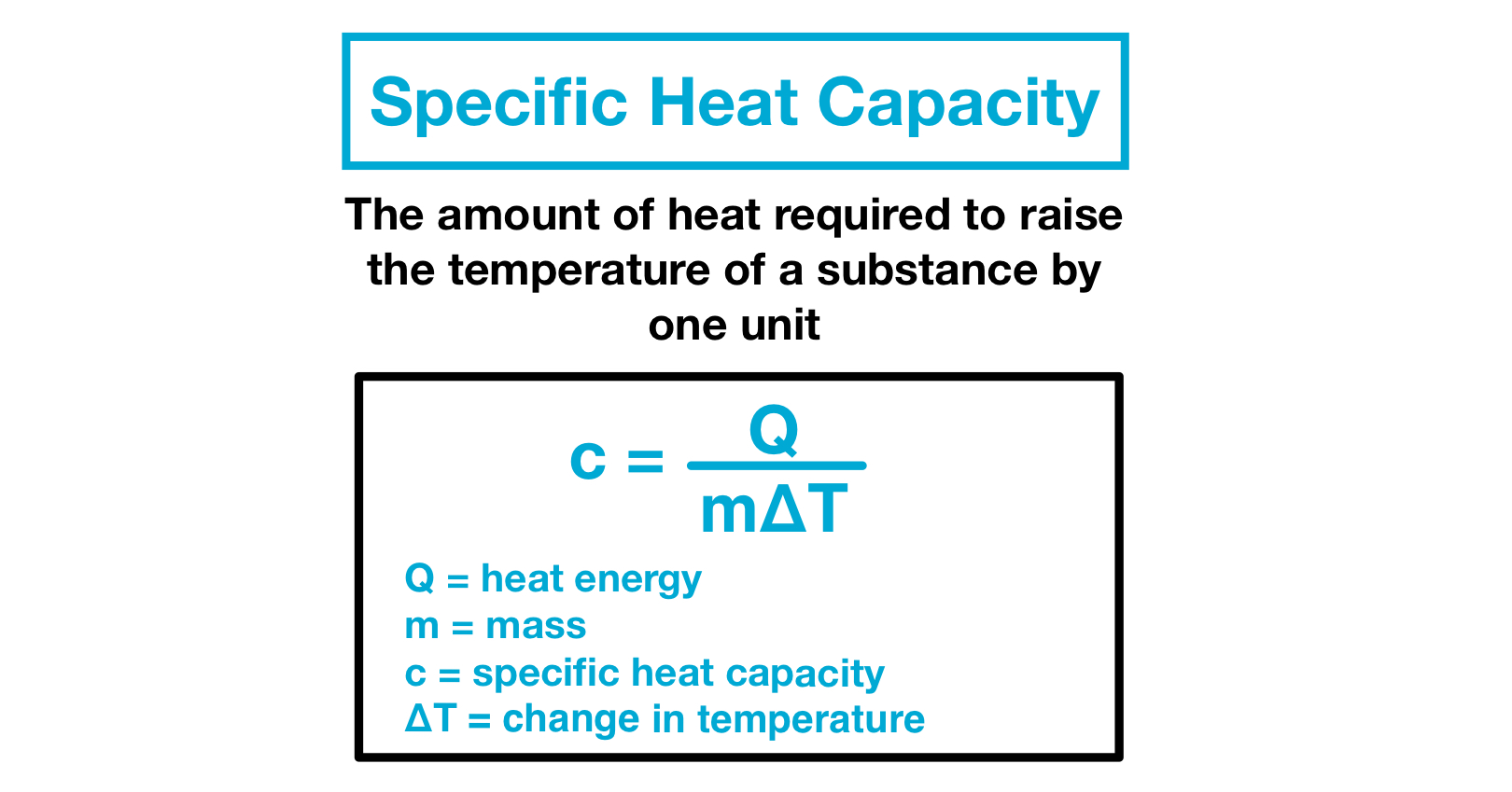
ΔT is a change in temperature. If youre given the amount of energy used the mass and initial temperature heres how to calculate the final temperature of a reaction. C p C p M and.
As per definition the heat capacity has a limited application because it is an extensive property meaning it will depend on the substances mass. Specific Heat Capacity is the heat required to raise temperature of the unit mass of a given substance by a given amount. Heat capacity has SI units J K-1.
Formula for Heat Capacity. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin JK. Specific heat the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one Celsius degree.
Heat capacity ratio of heat absorbed by a material to the temperature change. Specific heat does not depend on the mass of an object as it is defined per unit mass. Experiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated Temperatures 2011.
Heat capacity and Specific Heat capacity are always positive quantities. If we talk in SI. Common units used to express enthalpy are the joule calorie or BTU British Thermal Unit Enthalpy in a throttling process is constant.
Battery capacity is defined as the total amount of electricity generated due to electrochemical reactions in the battery and is expressed in ampere hours. For example a constant discharge current of 1 C 5 A can be drawn from a 5 Ah battery for 1 hour. Heat capacity is directly proportional to the mass of an object.
C p specific heat capacity. The heat capacity of a defined object is usually expressed in joules or calories and temperature in Kelvin or Celsius. Heat capacity is an extensive propertyThe corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity found by dividing the heat capacity of an object.
Commonly quoted and tabulated in the. The formula of molar heat capacity is as follows. Ahmet Aktaş Yağmur Kirçiçek in Solar Hybrid Systems 2021.
M molar weight of the actual substance gmol. Units it is the total amount of heat in joules required to raise the temperature of a substance 1 Mole usually by 1 Kelvin. The heat Capacity formula is expressed as the product of mass specific heat and change in the temperature which is mathematically given as.
It is the ratio of two specific heat capacities C p and C v is given by. Change in enthalpy is calculated rather than enthalpy in part because total enthalpy. The units of specific heat are usually calories or joules per gram per Celsius degree.
In Physics the specific heat capacity is commonly used. The specific heat capacity can be calculated from the molar heat capacity and vise versa. 1st Law of Thermodynamics - The First Law of Thermodynamics simply states.
Enthalpy is denoted as H. Q C m t is the formula for the specific heat capacity. ΔQ is the amount of heat energy.
The Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure C p Heat capacity at Constant VolumeC v The isentropic expansion factor is another name for heat capacity ratio that is also denoted for an ideal gas by γ gamma. Thermodynamics - Work heat and energy systems. For the same battery a discharge current of.
Specific Heat Capacity of Water is approximately 42 JgC. Therefore the ratio between C p and C v is the specific heat. Specific heat capacity.
A specific latent heat L expresses the amount of energy in the form of heat Q required to completely effect a phase change of a unit of mass m usually 1 kg of a substance as an intensive property. Material Properties - Material properties of gases fluids and solids - densities specific heats viscosities and more. Intensive properties are material characteristics and are not dependent on the size or extent of the sample.
S ΔQ mΔT. Molar specific heat capacity or molar heat capacity symbol. Cn is the total heat needed to raise a given substances temperature 1 Mole.
The SI unit of Specific Heat capacity is J kg1K1. This is the heat capacity thats normal to a unit of mass. It is usually expressed as calories per degree in terms of the actual amount of material being considered most commonly a mole the molecular weight in grams.
Where S is known as the Specific Heat Capacity. M is the mass of a substance. The Scottish scientist Joseph Black in the 18th century noticed that equal masses of.
Specific heat gives the heat capacity per kilogram of a substance. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. Thus it takes 42 joules of energy to raise 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius.
The heat needed to raise a substances temperature by 1 degree Celcius is called the specific heat capacity. The constant pressure of the specific heat capacity of steam is 18723 kJkg K. Therefore Specific Heat Capacity can be expressed as.
Specific enthalpy denoted as h. For example the specific heat of water is 1 calorie or 4186 joules per gram per Celsius degree. The specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat J absorbed per unit mass kg of the material when its temperature increases 1 K or 1 C and its units are Jkg K or Jkg C.
C p molar heat capacity. Methanol with molecular formula CH3OH has a molar heat capacity C p of 811 Jmol K.
Specific Heat Vs Heat Capacity

Specific Heat Capacity Youtube
Heat Capacity Of Water Overview Importance Expii

Specific Heat Definition Facts Britannica
0 Response to "Specific Heat Capacity Definition"
Post a Comment